Contents
Astrocytes: The Key Players in Stabilizing Emotional Memories in the Brain
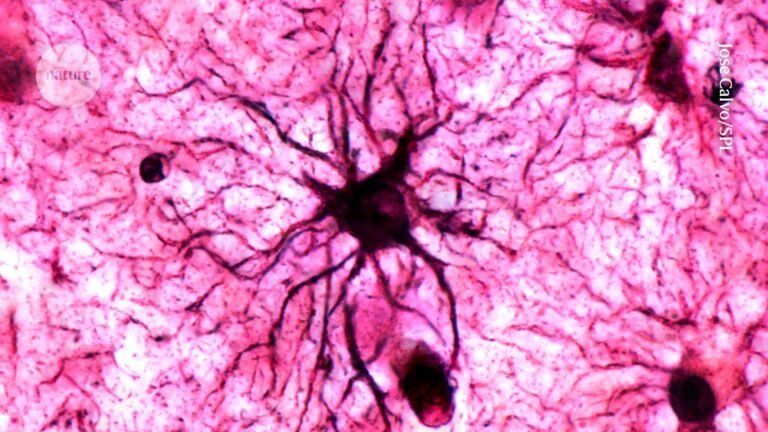
A recent study published in Nature has revealed that astrocytes, a type of brain cell, play a crucial role in stabilizing memories in the brain, particularly emotional ones. The findings suggest that astrocytes are not just supportive cells, but have an active role in storing memories for long-term recall, and could be a potential target for treating memory conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder and Alzheimer’s disease.
The question of how we remember emotional events so well has long been a topic of interest in the field of neuroscience. According to a study conducted by researchers at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science in Wako, Japan, astrocytes are the key players in stabilizing memories in the brain. The study, which was published in Nature, found that astrocytes have a much more active role in storing memories than previously thought, and can even be directly triggered by repeated emotional experiences. The researchers behind the study suggest that the cells could be a fresh target for treating memory conditions such as those associated with post-traumatic stress disorder and Alzheimer’s disease. The study’s co-author, Jun Nagai, a neuroscientist at RIKEN Center for Brain Science, explains that the study provides an answer to the question of how a specific memory is stored for the long term, and identifies how the brain selectively filters important memories at the cellular level.
Understanding Astrocytes and Their Role in Memory Stabilization
Astrocytes are a type of brain cell that were previously thought to simply support neurons in creating the physical traces of memories in the brain. However, the study found that they have a much more active role in storing memories for long-term recall. The researchers developed a method for measuring activation patterns in astrocytes across a whole brain of a mouse as it completes a memory task. They measured the upregulation of a gene called Fos, an early marker of cell activity that is associated with the physical traces of memories in the brain. The study found that astrocyte activity was more important for recalling past events than creating new memories.
The Importance of Astrocytes in Recalling Emotional Memories
In a well-established fear-conditioning memory task, mice learnt to associate a certain cage with unpleasant shocks to their feet while the researchers tracked the level of Fos in their brains. Days later, the animals would re-enter the cage and recall the unpleasant sensation. The researchers observed strong Fos upregulation in astrocytes in the animals’ amygdalas and other brain regions when mice re-entered the cage, but not during the initial learning phase. This suggests that astrocyte activity was more important for recalling past events than creating new memories. According to Nagai, “The surprise was that astrocytes did not respond to the fear experience the first time, only the second time.”
Some key highlights of the study include:
* Astrocytes play a crucial role in stabilizing memories in the brain, particularly emotional ones.
* Astrocytes have an active role in storing memories for long-term recall, and can even be directly triggered by repeated emotional experiences.
* The study suggests that astrocytes could be a potential target for treating memory conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder and Alzheimer’s disease.
* The researchers developed a method for measuring activation patterns in astrocytes across a whole brain of a mouse as it completes a memory task.
* The study found that astrocyte activity was more important for recalling past events than creating new memories.
As Nagai explains, “We provide an answer to the question of how a specific memory is stored for the long term. By studying astrocytes, we identify how the brain selectively filters important memories at the cellular level.” The study’s findings have significant implications for our understanding of how memories are stored and recalled, and could lead to new treatments for memory conditions.
Implications of the Study and Future Directions
The study’s findings have significant implications for our understanding of how memories are stored and recalled, and could lead to new treatments for memory conditions. According to the researchers, the study suggests that astrocytes could be a potential target for treating memory conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder and Alzheimer’s disease. The study’s findings also highlight the importance of astrocytes in recalling emotional memories, and suggest that they play a crucial role in stabilizing memories in the brain.
Some potential future directions for research include:
* Investigating the role of astrocytes in other types of memory, such as spatial memory and working memory.
* Examining the relationship between astrocytes and other brain cells, such as neurons and microglia.
* Developing new treatments for memory conditions that target astrocytes.
In conclusion, the study published in Nature has revealed that astrocytes play a crucial role in stabilizing memories in the brain, particularly emotional ones. The findings suggest that astrocytes are not just supportive cells, but have an active role in storing memories for long-term recall, and could be a potential target for treating memory conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder and Alzheimer’s disease. As researchers continue to study the role of astrocytes in memory, we may uncover new insights into how memories are stored and recalled, and develop new treatments for memory conditions.
Keywords: astrocytes, brain cells, memory stabilization, emotional memories, post-traumatic stress disorder, Alzheimer’s disease, neuroscience, memory recall, brain research, cellular biology.
Hashtags: #astrocytes #braincells #memorystabilization #emotionalmemories #PTSD #Alzheimers #neuroscience #memoryrecall #brainresearch #cellularbiology.
Source link